Financial Markets Overview
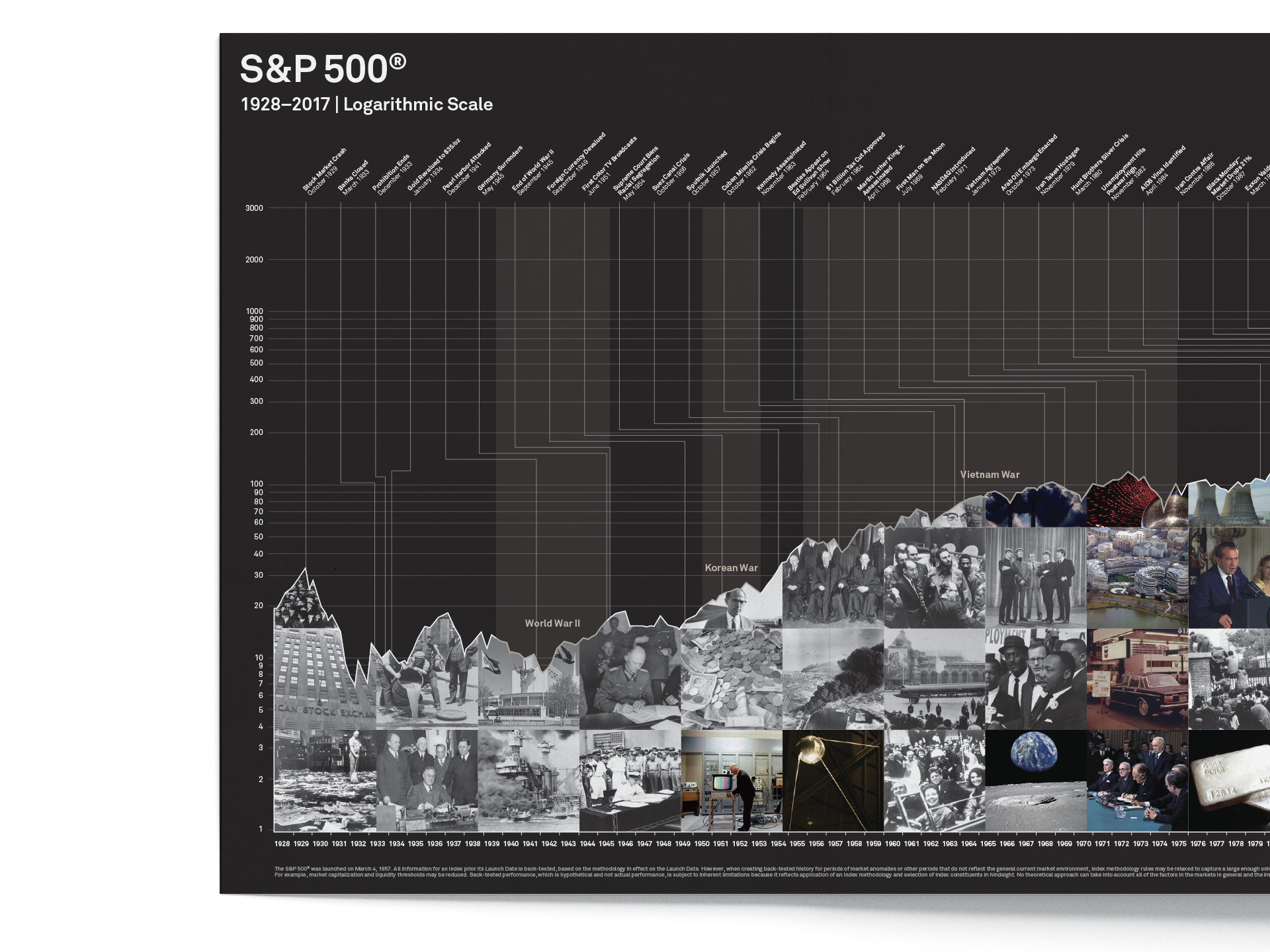
The global financial markets continue to evolve with a dynamic interplay of economic indicators, investor sentiment, and geopolitical developments. From stock indices to commodity prices, the market landscape is shaped by a variety of factors that influence trading decisions and investment strategies.
Key Market Indices
Major stock indices such as the S&P 500, Dow Jones, and Nasdaq have shown mixed performance, reflecting the ongoing balance between optimism and caution among investors. The S&P 500 has seen a slight increase, while the Nasdaq remains relatively stable. These movements are often influenced by earnings reports, macroeconomic data, and shifts in monetary policy.
- S&P 500: Recent gains indicate a cautious optimism among investors, with a focus on growth stocks.
- Dow Jones: The index has experienced moderate gains, suggesting a broader market recovery.
- Nasdaq: While showing smaller gains, it remains sensitive to changes in technology sector performance.
Commodity Markets
Commodities remain a critical component of the financial landscape, with prices fluctuating based on supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical tensions, and economic conditions. Gold and silver, in particular, have attracted attention due to their perceived safe-haven status during times of uncertainty.
- Gold Futures: Recently, gold prices have risen, indicating increased demand for safe-haven assets.
- Silver Futures: Silver has also seen a notable increase, driven by both industrial demand and speculative interest.
Currency Exchange Rates
Currency exchange rates are influenced by a range of factors, including interest rate differentials, inflation expectations, and central bank policies. Major currencies such as the US Dollar, Euro, and Japanese Yen have experienced varying degrees of strength and weakness.
- USD/JPY: This pair has shown volatility, reflecting the impact of monetary policy decisions from the Federal Reserve and the Bank of Japan.
- EUR/USD: The euro has faced pressure due to divergent economic performances between the Eurozone and the United States.
Market Trends and Analysis
Investors are closely monitoring market trends, seeking insights into potential opportunities and risks. Analysts often use technical analysis and fundamental data to forecast future movements, helping traders make informed decisions.
Technical Analysis
Technical indicators such as moving averages, support and resistance levels, and candlestick patterns provide valuable insights into market behavior. These tools help traders identify potential entry and exit points.
- Moving Averages: The 50-day and 200-day moving averages are key indicators used to gauge trend direction.
- Candlestick Patterns: Patterns like the bullish engulfing and bearish harami can signal potential reversals.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating a company's financial health, industry position, and economic environment. Investors often look at metrics such as earnings, revenue growth, and debt levels to assess a company's value.
- Earnings Reports: Strong earnings can lead to positive stock price movements, while weak results may cause declines.
- Economic Indicators: Data such as GDP growth, employment figures, and inflation rates can impact market sentiment.
Investment Strategies
With the complexity of the financial markets, various investment strategies have emerged to cater to different risk appetites and goals. From long-term value investing to short-term trading, each approach has its own set of advantages and challenges.
Value Investing
Value investing focuses on identifying undervalued stocks that have strong fundamentals but are trading below their intrinsic value. This strategy often involves a long-term perspective and patience.
- Key Metrics: Price-to-earnings ratio, price-to-book ratio, and dividend yield are commonly used to evaluate value stocks.
- Examples: Companies like Coca-Cola and Johnson & Johnson are often cited as examples of value stocks.
Growth Investing
Growth investing targets companies that are expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to the market. These stocks often have higher price-to-earnings ratios and are typically found in sectors like technology and healthcare.
- Key Metrics: Revenue growth, earnings growth, and market share are important indicators for growth stocks.
- Examples: Companies like Tesla and Amazon are often considered growth stocks.
Conclusion
The financial markets are a complex and ever-changing landscape, influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding these dynamics is essential for investors looking to navigate the markets effectively. By staying informed and employing sound strategies, investors can better manage risks and capitalize on opportunities. As the market continues to evolve, the importance of continuous learning and adaptation cannot be overstated.

0 comments:
Post a Comment